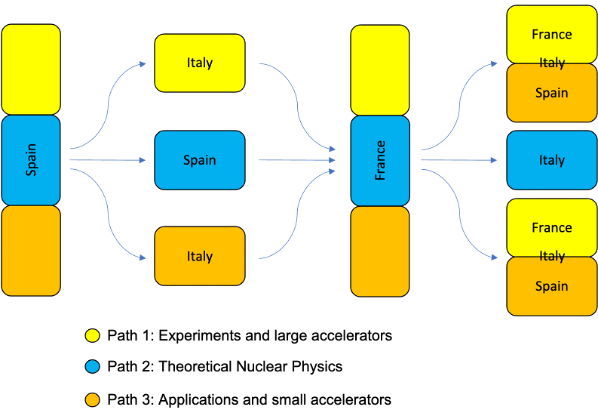
There will be three specialization paths:
- PATH 1: Experiments and Instrumentation in large accelerators. Students following this path (1/3 approx) will start in Spain for S1, will move to Padova for S2, then to France for S3 and, finally, will go to any University in the consortium or associated center for the Master Thesis in S4.
- PATH 2: Theoretical nuclear physics. Students within this path (1/3 approx) will start in Spain for S1 & S2, then to will go to France for S3 and, finally to Italy (Padova or Catania) for the Master Thesis in S4.
- PATH 3: Applications and small accelerators. Students within this path (1/3 approx) will start in Spain for S1, will move to Catania for S2, then to France for S3 and, finally, will go to any University in the consortium or associated partner for the Master Thesis in S4.
S1 S2 S3 S4
The general scheme ECTs distribution of the Course is presented in the following table, giving the number of credits associated to each module according to the mobility and specialization path:
PATH 1 - EXP: Large accelerators (~1/3 of the students*)
PATH 2 - THEO: Theoretical Nuclear Physics (~1/3 of the students*)
PATH 3 - APP: Small accelerators (~1/3 of the students*)
*) Experience coming from previous editions makes us to estimate that the number of students coming to paths 1, 2 and 3 are approx. equally distributed among the paths.
| MOD1 | MOD2 | MOD3 | MOD4 | MOD5 | ||
| EXP | THEO | APP |
|
|
| |
PATH 1 | 30 | 24 | 12 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 30 |
PATH 2 | 30 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 6 | 12 | 30 |
PATH 3 | 30 | 6 | 6 | 30 | 6 | 12 | 30 |
Total | 30 | 42 | 6 | 12 | 30 | ||
Concerning contents, the academic programme is structured in 5 modules:
Module 1: Basics nuclear physics and tools (30 ECTs in S1)
Module 1 (BAS) will be devoted to the transversal knowledge required on general Nuclear Physics, and Complementary/Interdisciplinary courses adapted to the chosen path (notably numerical methods and computing). These courses will be concentrated in the first year, in S1, and include topics as Quantum Mechanics, Basic Nuclear Physics: theory and laboratory, Computing and Numerical Methods, and Atomic and Plasma Physics
Module 2: Advanced nuclear physics (42 ECTs in S2 and S3), with three specialties (experimental, theory, applications)
Module 2 allows students to follow 3 paths: Experimental/large accelerators (path 1), Theoretical (path 2), or Applied/small accelerators (path 3). This module will give the specialized focus of the Master curriculum towards fundamental or applied nuclear physics. Fundamental physics includes either an experimental or a theoretical focus. Applied physics is especially focused on biomedical applications, but also includes fundamentals in accelerators technology. The specialization is progressive, starting already in the first year (S2), then continuing in S3 with courses and specific internships, to finalize in S4 with the master thesis. Academic topics in S2 and S3 include Nuclear Structure and Reactions, Nuclear Astrophysics, Weak and Strong Interactions, Collision Physics, Many Body Theory, Nuclear Physics Applications: Art, Materials, Radiation protection, radiotherapy and the physics of medical devices, Metrology and Data Analysis, Experimental Nuclear Physics, Advanced Nuclear and Subnuclear Laboratory, and Accelerator Physics and Advanced Instrumentation.
Module 3: Common advanced course (S3 course, 6 ECTs)
Module 3 (ADV) is devoted to a highly specialized topic that will be selected for each intake among the hot topics in Nuclear Physics. During two weeks at the end of S3 this special topic will be presented by invited scholars in Caen, France. The choice of period and location is done to optimize the mobility scheme of the students (see below). At present, we have decided to continue the previous programme on “Data Analysis and Machine Learning”, and we are in the process of setting an updated detailed programme as well as the teachers in charge of the course.
Module 4: Internship (12 ECTs)
Module 4 (INTERNSHIP) will be done in the third semester (S3). It is dedicated to student internship (experimental, theoretical or applied topics are accepted), which will take place in different institutional or industrial research centres in Caen (France) according to the chosen path and desired specialization. Students will work in teams of two, will be supported by internal (Consortium) and external (Associated Members) tutoring and will be fully integrated in the research centres within appropriate signed agreements during the whole semester (from September to December), where they will perform their internship project part-time. The internships are programmed by the University in advance, so as to provide real working experience, valuable for future job placement.
Module 5: Master Thesis (30 ECTs)
Module 5 (THESIS) will include the initial steps to write a short project of Master Thesis which has to be approved by the Master Academic Committee and the conduction of a research work in theoretical, experimental or applied Nuclear Physics with the direction of one or more advisors from one or more Universities (works with coordinate tutors from two partner Universities, or from one University and one associated industrial/host institution, will be encouraged).
The list the courses offered in each University for semesters one, two and three each year is given in the table below for each path separately. Concerning semester 3, only 12 ECTS have to be obtained in regular courses, since 12 ECTS correspond to the internship and 6 ECTS are assigned to a common course (module 3, see below) which is compulsory for all students. Semester 4 is devoted to the preparation of the Master thesis in a host University, research center or company (MOD 5):
MOD. 1 - Basic nuclear physics and tools | MOD. 2 - Advanced nuclear physics (EXP) | MOD. 2 - Advanced nuclear physics (THEO) | MOD. 2 - Advanced nuclear physics (APP) | MOD. 3 -Common Specialized Course | MOD. 4 - Internship | MOD. 5 - Master Thesis |
PATH 1: Experiments, instrumentation and large accelerators
S1: Spain | Computing and Numerical Methods (6) | Quantum Mechanics (6) | Basic Experimental and Applied Laboratory (6) | Nuclear Structure (6) | Atomic & Plasma Physics (6) |
S2: Padova (Italy) | Radioactivity and Nuclear Measurements (6) | Nuclear Astrophysics (6) | Heavy-Ion Reactions (6)
| Accelerator Physics (6)
| And 1 to 2 courses **) among -Advanced Laboratory (6) -Sub Nuclear Physics (6) - Introduction to Radiation Detectors (6) -Astroparticle Physics (6) |
S3: Caen (France) | Research Internship (12) | Common Advanced Course (6) | Experimental Nuclear Physics (12) * | ||
S4: Spain, France or Italy | Master thesis on experimental nuclear physics, instrumentation large accelerators (30) | ||||
* Experimental nuclear physics includes: design of nuclear experiments, ions and sources, metrology, and Monte Carlo simulations.
** If two courses are chosen here one of the previous four should be removed
PATH 2: Theoretical nuclear physics
S1: Spain | Computing and Numerical Methods (6) | Quantum Mechanics (6) | Basic Experimental and Applied Laboratory (6) | Nuclear Structure (6) | Atomic & Plasma Physics (6) |
S2: Spain | Introduction to Nuclear Reactions (6) | Relativistic Quantum Mechanics (6) | Hadronic Physics (6) or Nuclear Astrophysics (6) | Weak Interactions (6) | Many-Body Theories in Nuclear Physics (6) |
S3: Caen (France) | Research Internship (12) | Common Advanced course (6) | Theoretical nuclear and atomic physics (12)* | ||
S4: Italy | Master thesis on theoretical nuclear physics (30) | ||||
* Theoretical nuclear and atomic physics includes: advanced nuclear theory, density functional theory and applications, and fundamental interactions
PATH 3: Applications and small accelerators
S1: Spain | Computing and Numerical Methods (6) | Quantum Mechanics (6) | Basic Experimental and Applied Laboratory (6) | Nuclear Structure (6) | Atomic & Plasma Physics (6) |
S2: Catania (Italy) | Nuclear Reaction Theory (6) | Accelerator Physics and applications (6) | Advanced Nuclear Techniques for Radioprotection (6)
| Physics for Diagnostics and Therapy (6) / Environmental Radioactivity (6) | Nuclear Astrophysics (6) |
S3: Caen (France) | Research Internship (12) | Common Advanced course (6) | Applications for therapy (12)* | ||
S4: Spain, France or Italy | Master thesis on applications and small accelerators (30) | ||||
* Applications for therapy includes: physics of medical devices, dosimetry and radiation protection, basics of radiotherapy.
Courses will be taught in English. Students will be provided with the appropriate academic material in English.
All six participant Universities will offer Master thesis. In addition to the participant Universities, the associated Labs and Companies can be the hosts for Master Thesis development in cooperation with the host university. In particular, the following associated research centres could be the host for students: CERN (Geneva, Switzerland), the National Laboratory at Legnaro (Padova, Italy), National Laboratory del Sud (Catania, Italy), National Accelerator at GANIL (Caen, France), GSI Accelerators (Darmstadt, Germany), National Centre Accelerator (Seville, Spain), Accelerator Centre at Madrid (Madrid, Spain), CSIC (IEM, Madrid and IFIC, Valencia), CIEMAT (Madrid, Spain), INFN-LNF Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (Frascati, Italy), TRIUMF (Canada), TANDAR (Argentina), UNAM (México), CNESTEN (Morocco), iThemba Labs. (South Africa), etc. This list can be extended when other relevant institutions may join the consortium as associated partners.
